On Monday 17th October 1814, a terrible disaster claimed the lives of at least 8 people in St Giles, London. A bizarre industrial accident resulted in the release of a beer tsunami onto the streets around Tottenham Court Road.
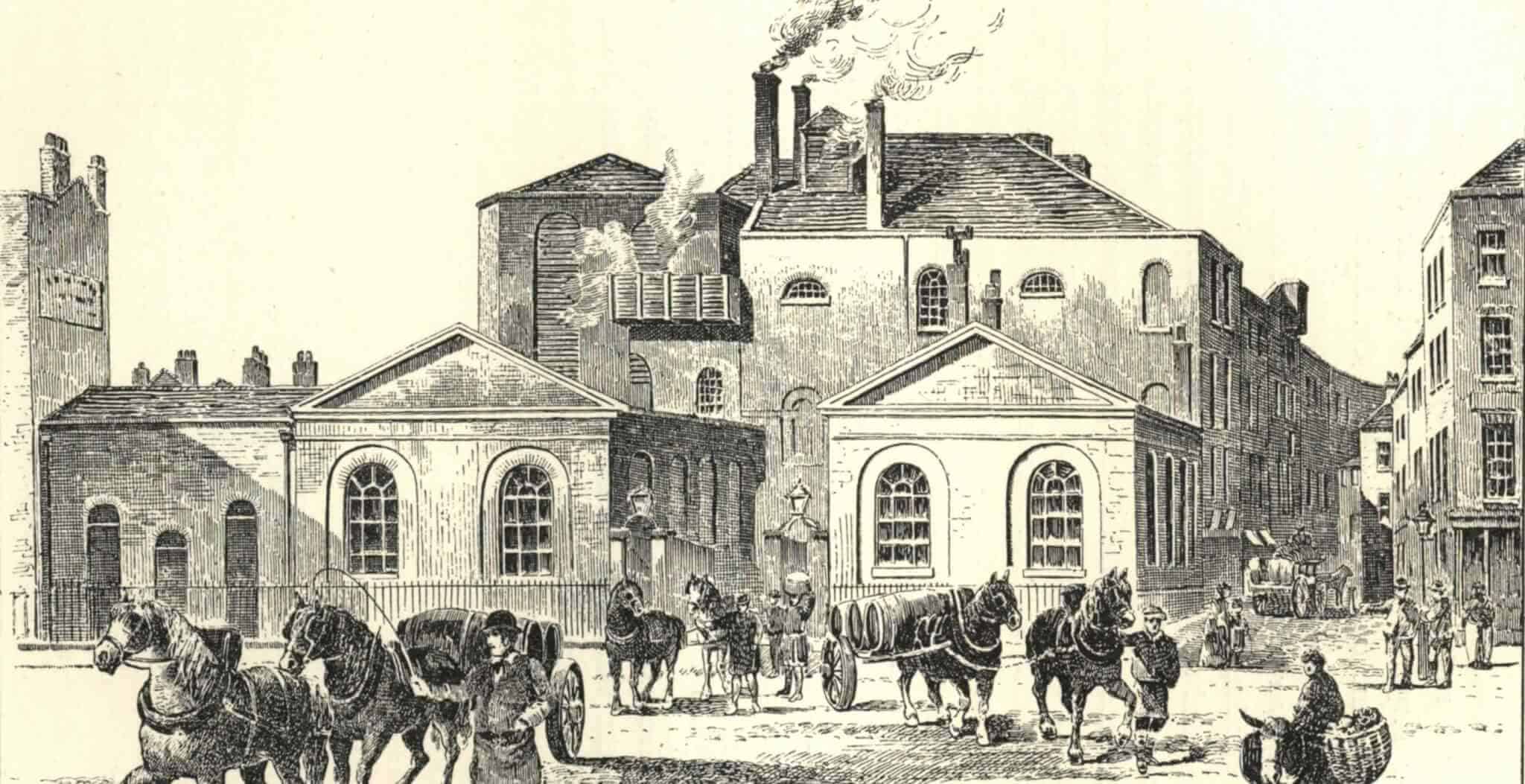
The Horse Shoe Brewery stood at the corner of Great Russell Street and Tottenham Court Road. In 1810 the brewery, Meux and Company, had had a 22 foot high wooden fermentation tank installed on the premises. Held together with massive iron rings, this huge vat held the equivalent of over 3,500 barrels of brown porter ale, a beer not unlike stout.
On the afternoon of October 17th 1814 one of the iron rings around the tank snapped. About an hour later the whole tank ruptured, releasing the hot fermenting ale with such force that the back wall of the brewery collapsed. The force also blasted open several more vats, adding their contents to the flood which now burst forth onto the street. More than 320,000 gallons of beer were released into the area. This was St Giles Rookery, a densely populated London slum of cheap housing and tenements inhabited by the poor, the destitute, prostitutes and criminals.
The flood reached George Street and New Street within minutes, swamping them with a tide of alcohol. The 15 foot high wave of beer and debris inundated the basements of two houses, causing them to collapse. In one of the houses, Mary Banfield and her daughter Hannah were taking tea when the flood hit; both were killed.
In the basement of the other house, an Irish wake was being held for a 2 year old boy who had died the previous day. The four mourners were all killed. The wave also took out the wall of the Tavistock Arms pub, trapping the teenage barmaid Eleanor Cooper in the rubble. In all, eight people were killed. Three brewery workers were rescued from the waist-high flood and another was pulled alive from the rubble.
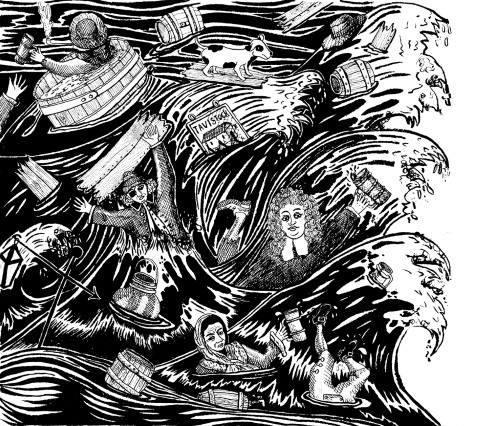

All this ‘free’ beer led to hundreds of people scooping up the liquid in whatever containers they could. Some resorted to just drinking it, leading to reports of the death of a ninth victim some days later from alcoholic poisoning.
‘The bursting of the brew-house walls, and the fall of heavy timber, materially contributed to aggravate the mischief, by forcing the roofs and walls of the adjoining houses.‘ The Times, 19th October 1814.
Some relatives exhibited the corpses of the victims for money. In one house, the macabre exhibition resulted in the collapse of the floor under the weight of all the visitors, plunging everyone waist-high into a beer-flooded cellar.
The stench of beer in the area persisted for months afterwards.
The brewery was taken to court over the accident but the disaster was ruled to be an Act of God, leaving no one responsible.
The flood cost the brewery around £23000 (approx. £1.25 million today). However the company were able to reclaim the excise duty paid on the beer, which saved them from bankruptcy. They were also granted ₤7,250 (₤400,000 today) as compensation for the barrels of lost beer.
This unique disaster was responsible for the gradual phasing out of wooden fermentation casks to be replaced by lined concrete vats. The Horse Shoe Brewery was demolished in 1922; the Dominion Theatre now sits partly on its site.